IOPA:
Dental IOPA, or Intraoral Periapical radiography, is a diagnostic imaging technique commonly used in dentistry to capture detailed images of individual teeth and surrounding structures also used for Full Mouth X-ray in Kukatpally. The primary purpose of IOPA is to evaluate the health of the roots of teeth and their supporting bone, facilitating the diagnosis of various dental conditions, including periapical infections, fractures, and developmental anomalies. During the procedure, a small X-ray film or digital sensor is placed inside the mouth, close to the targeted tooth, while the X-ray machine is positioned outside. The resulting radiographs provide a clear view of the tooth's root length and surrounding bone, helping dentists assess the need for treatments such as root canal therapy, extractions, or implants. Best IOPA (RVG) X-ray in Hyderabad is valuable for its ability to deliver focused and high-resolution images with minimal radiation exposure compared to other imaging methods. Its role is pivotal in routine dental examinations and in monitoring specific issues, making it an essential tool in modern dental practice for enhancing patient care and outcomes.
RVG:
Dental RVG, or digital radiovisiography, is an advanced imaging technique used in dentistry to obtain high-quality radiographs of teeth and surrounding structures. This technology replaces traditional film-based x-rays with digital sensors, allowing for immediate image acquisition, enhanced diagnostic capabilities, and improved patient comfort. The RVG system or Dental X-ray in Kukatpally works by capturing radiographic images directly onto a computer, which not only streamlines the imaging process but also minimizes radiation exposure compared to conventional methods. The digital images can be easily manipulated—adjusting brightness, contrast, and magnification—enabling dentists to detect cavities, bone loss, and other dental conditions with greater accuracy. Additionally, these images can be stored electronically, facilitating better patient record management and easier sharing among dental professionals. The use of RVG technology also supports more efficient patient communication, as dentists can visually present findings and treatment plans. Overall, dental RVG at Best Dental Hospital in Hyderabad represents a significant advancement in dental diagnostics, enhancing the quality of care delivered to patients while promoting a more efficient workflow in dental practices.
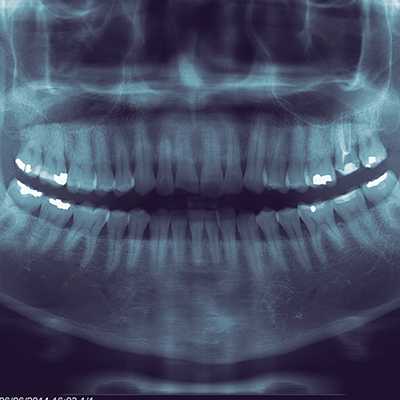
OPG
A full mouth X-ray, often referred to as an Orthopantomogram (OPG), is a panoramic imaging technique that captures the entire dentition in a single image. This type of radiograph provides a comprehensive view of the teeth, jawbone, and surrounding structures, making it an essential tool in dental diagnostics. The OPG is especially useful for identifying dental issues such as cavities, impacted teeth, periodontal disease, and jaw abnormalities. The procedure is relatively quick, requiring the patient to bite down on a specialized film holder while the X-ray machine rotates around their head. It emits a low dose of radiation and is generally safe for patients. The resulting image gives dental professionals a broader perspective, aiding in treatment planning, monitoring oral health, and facilitating the detection of conditions that may not be visible in standard intraoral X-rays. OPGs are particularly beneficial in orthodontics, oral surgery, and general dentistry for evaluating tooth alignment and planning extractions or implants. Regular use of OPG can play a critical role in maintaining oral health and ensuring appropriate timely interventions.

